Databases Guide¶
Databases are very important and crucial part of any systems, they provide an efficient way to store, retrieve and analyze data.
The teracy-dev VM provides some of the most popular databases such as: MySQL, PostgreSQL
and MongoDB. This guide will help us to enable and use these databases.
MySQL¶
MySQL is installed by default on the teracy-dev VM with root as username and teracy
as password by default.
Local access
$ vagrant ssh $ mysql -u root -pteracy
And you should see the following output:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 5 Server version: 5.5.41-0ubuntu0.12.04.1 (Ubuntu) Copyright (c) 2000, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql>
Type
$ exitto exit theMySQLshell above.Remote access
For easier development,
MySQLon the teracy-dev has binding address of0.0.0.0, this means that you could remote access it.The teracy-dev VM by default forwards the port 3306 of
MySQLto 6603 of the host machine. So you’re going to remote access with the following credentials information by default:- host: the guest machine’s IP address or
127.0.0.1to access from the guest machine - port:
6603 - username:
root - password:
teracy
We need a
MySQLclient, such as MySQL Command-Line Tool, MySQL Workbench, etc.With MySQL Command-Line Tool to remote access from the guest machine:
$ mysql -u root -pteracy -h 127.0.0.1 -P 6603With MySQL Workbench to remote access from the guest machine:
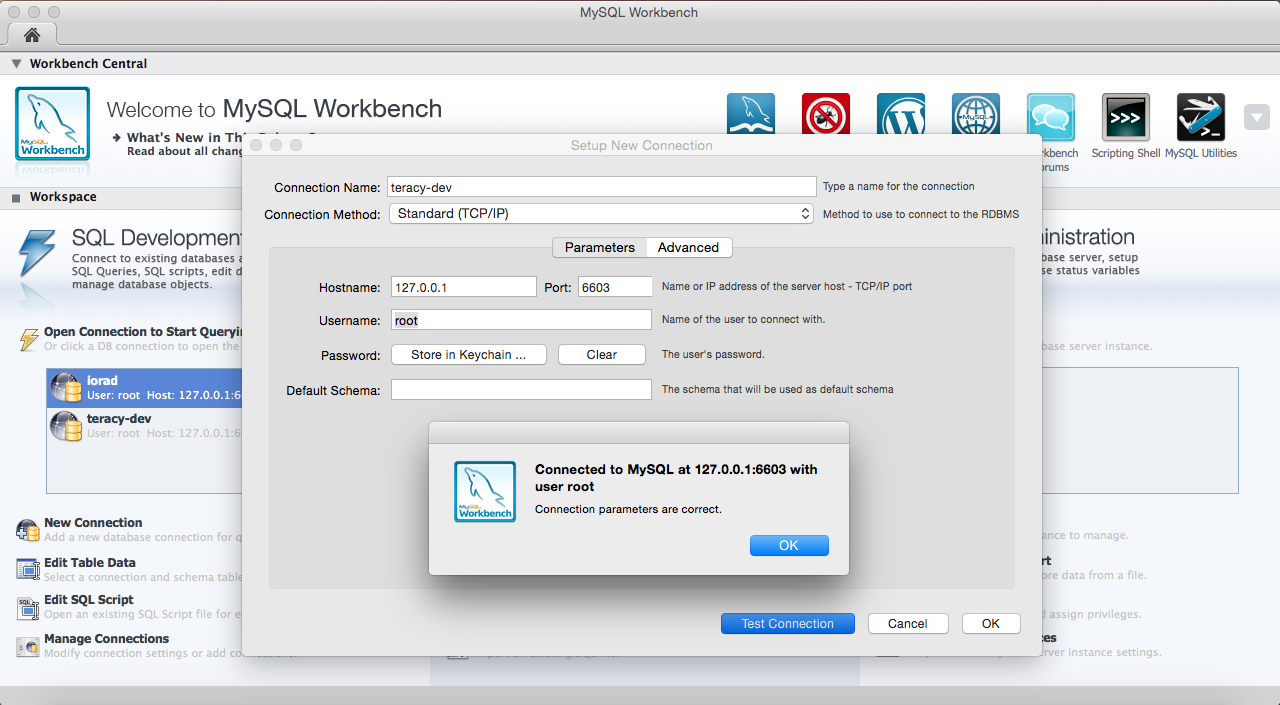
- host: the guest machine’s IP address or
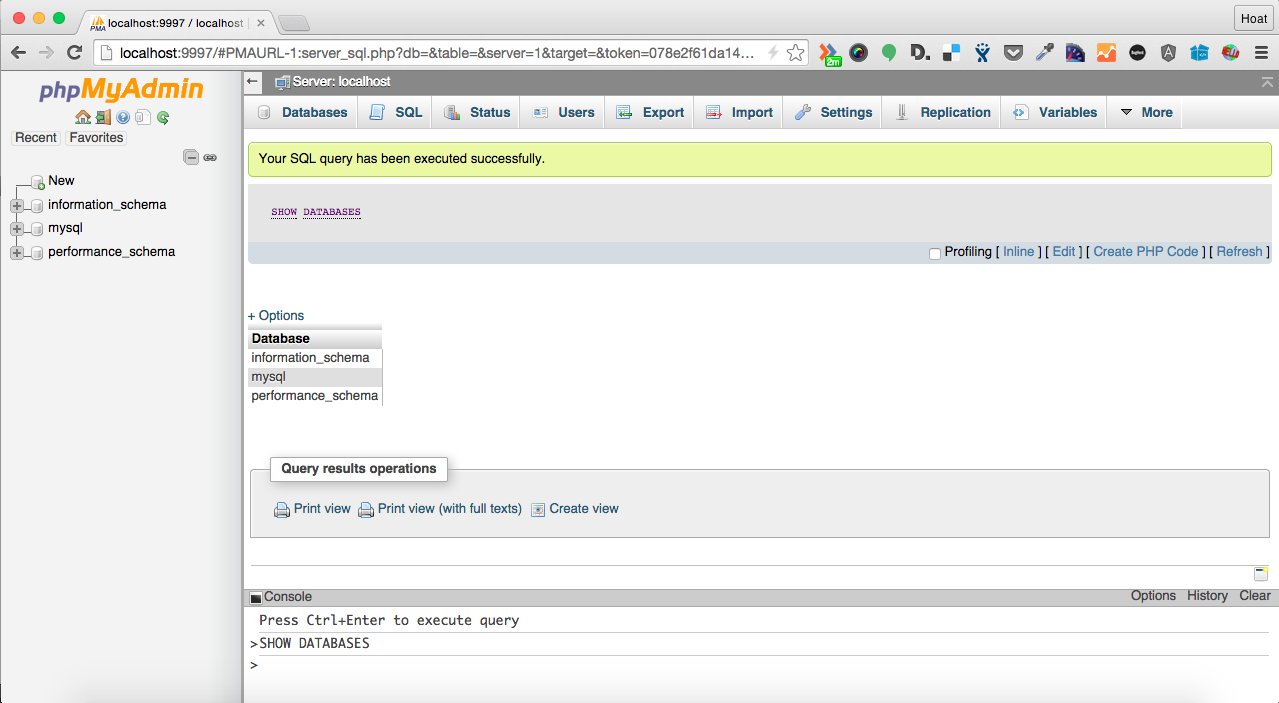
phpMyAdmin
Open http://localhost:9997 and type root as username, teracy as password and you’re done.
From now on you can start digging MySQL database at: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/
PostgreSQL¶
PostgreSQL is disabled by default on the teracy-dev VM:
{
"postgresql":{
"enabled":false,
"password":{
"postgres":"teracy"
},
"version":"9.3"
}
}
Enable
To enable, you need to override the default configuration by appending postgresql attribute within teracy-dev attribute to the vagrant_config_override.json file like the configuration below:
{ "chef_json":{ "teracy-dev":{ "postgresql":{ "enabled":true } } } }
Save the file and then
$ vagrant provision, after thatPostgreSQLshould be installed.By default, we use postgres as username and teracy as password to access the enabled
PostgreSQLdatabase instance.Verify
Within vagrant ssh session, by:
$ vagrant ssh $ psql -U postgres -h localhost
Type teracy when being prompted for the password:
Password for user postgres:And you should see the following output:
psql (9.1.14) SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA, bits: 256) Type "help" for help. postgres=#
To exit the
PostgreSQLshell:postgres=# \q
Initialize the super user vagrant role and default vagrant database
This step is required for the first time when the
PostgreSQLdatabase is enabled and installed.$ sudo su postgres $ createuser vagrant
Type
yand hit enter when asked “Shall the new role be a superuser?”Now you can exit the su subshell to go back to the vagrant user SSH session:
$ exit
Now create vagrant database:
$ createdb vagrantLocal access
When vagrant super user and vagrant database is created, you just need to type:
$ psqlAnd you should see the the following output:
psql (9.1.14) Type "help" for help. vagrant=#
Type
\qto quit thePostgreSQLshell.Remote access
Todo
We need to support this by https://issues.teracy.org/browse/DEV-221
From now on you can start digging PostgreSQL database at: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/
MongoDB¶
MongoDB is disabled by default on the teracy-dev VM:
{
"mongodb":{
"enabled":false,
"version":"2.6.3"
}
}
Enable
To enable, you need to override the default configuration by appending mongodb attribute within teracy-dev attribute to the vagrant_config_override.json file like the configuration below:
{ "chef_json":{ "teracy-dev":{ "mongodb":{ "enabled":true } } } }
Save the file and then
$ vagrant provision, after thatMongoDBshould be installed.Verify
Within vagrant ssh session, by:
$ vagrant ssh $ mongo
And you should the the following output:
MongoDB shell version: 2.6.9 connecting to: test >Type
exitto quit theMongoDBshell.Local access
Just type
mongoand you’re done.Remote access
By default, the default port 27017 is forwarded to the guest machine, to remote access it, you only need to specify the host ip address when required:
- host: the guest machine’s IP address or 127.0.0.1 or localhost or none to access from the guest machine
For example, from a guest machine:
$ mongoor:
$ mongo localhostWe could replace localhost with 127.0.0.1.
or from a different machine to the machine running the teracy-dev VM with ip: 192.168.1.111
$ mongo 192.168.1.111
From now on you can start digging MongoDB database at: http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/